Answer ALL questions
Some questions must be answered with a cross in a box ( ). If you change your mind about an answer, put a line through the box ( )and then mark your new answer with a cross .
1 Using the Sun
(a) A student uses a converging lens to make an image of the Sun.
R to the right of P and on the dotted line
|
(i) Complete the sentence by putting a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer.
The lens forms a real image of the Sun at P, where the light rays cross.
The distance d is the (1)
ÿ A focal point
ÿ B focal lengthþ
ÿ C object length
ÿ D object distance
(ii) Radiation from the Sun includes some infrared waves. The lens bends infrared waves less than it does ordinary light.
Label, with an R, a place on the diagram where the infrared rays could cross. (1)
(d) The Electromagnetic spectrum.
(i) Fill in the missing waves in the Electromagnetic spectrum (1)
All three needed for 1 mark
Radio-waves
|
Microwave
|
Infra red
|
Visible light
|
Ultra violet
|
x-rays
|
Gamma rays
|
increasing frequency -------------------------------------------------------------------------->
(ii) Draw a labelled arrow under the diagram to show increasing frequency. (1)
(c) In some countries, infrared rays from the Sun are used to cook food. Light and infrared rays are both focused using a converging mirror.
(i) State what happens to the rays at S. (1)
…The rays are reflected
(ii) Explain why the light rays and infrared rays converge towards the same point. (2)
Both types of rays must obey the law of reflection, as the angles of incidence are the same for both types of ray, so are the angles of reflection. They are therefore brought to a focus at the same point
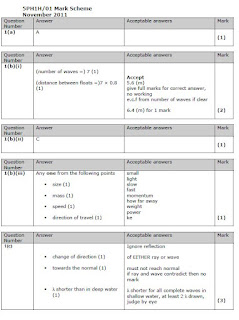
(iii) The infrared waves travel at a speed of 300 000 km/s. They take 500 s to travel from the Sun to the Earth. Calculate the distance between the Earth and the Sun. (3)
Velocity (v) = Distance (d) /time (t)
Rearranging d = v x t v = 300 000 km/s t = 500s
d = 300 000 x 500
d = 150 000 000 km
note only 2 marks possible without the workings
distance = 150 000 000. km
(Total for Question 1 = 10 marks)
2 Galaxies and the Universe
A scientist is observing the light waves emitted from a distant galaxy.
(a) Which of these statements is not true for light waves?
Put a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. (1)
ÿ A light waves transfer matter x
ÿ B light waves transfer energy
ÿ C light waves can transfer information
ÿ D light waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation
(b) The light detected by the scientist has a wavelength of 6.56 x 10-7 m and a frequency of 4.57 x 1017Hz.
Calculate the speed of light.
Use your formula sheet Show all your working (2)
V= fλ f = 4.57 x 1017 Hz λ = 6.56 x 10-7 m
V = (4.57 x 1017) (6.56 x 10-7)
V = 3 x 1011 m/s
(This is not the speed of light which is 3 x 108 m/s. The question correctly states the wavelength of visible light. You can work out the correct frequency for yourself)
Wave speed = 3 x 1011 m/s
(c) A galaxy is a collection of stars. Stars with a similar mass to our Sun will evolve to become red giants, before finally becoming white dwarfs at the end of their life.
What will stars with a mass greater than the Sun become at the end of their life? (2)
The end state of a star with a greater mass than the sun is either a neutron star or a black hole
(d) The Big Bang theory is the currently accepted theory of how the Universe started.
Described how the Universe began according to this theory. (1)
The whole of the current universe (space, matter, energy and time) was compressed into a point of almost zero volume. It has since expanded into the universe we observe today.
*(e) Red-shift and cosmic microwave background radiation are both strong pieces of evidence in support of the Big Bang theory.
Explain how the evidence of red-shift and cosmic microwave background radiation have led to the Big Bang theory being the currently accepted theory of how the Universe began.
(6)
REDSHIFT
The theory of the big bang predicts that the universe must be expanding.
All galaxy clusters show a redshift. This means they are travelling away from us.
The further the distance to the galaxy cluster the greater the redshift.
This tells us that the velocity of these galaxy clusters increases with distance from us.
This evidence fits in with an expanding universe
COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND RADIATION
The big bang theory predicts the early universe was very hot and very dense. There should be energy left over from this time.
The CMBR is a microwave signal that comes from space. It is the same in all directions. The signal is the energy from the hot young universe. As the universe has expanded the wavelength of these electromagnetic waves has been stretched so they now lie in the microwave band.
The redshift of the galaxies and the CMBR are both predicted by the big bang theory. This is why it is generally accepted
(Total for Question 2 = 12 marks)